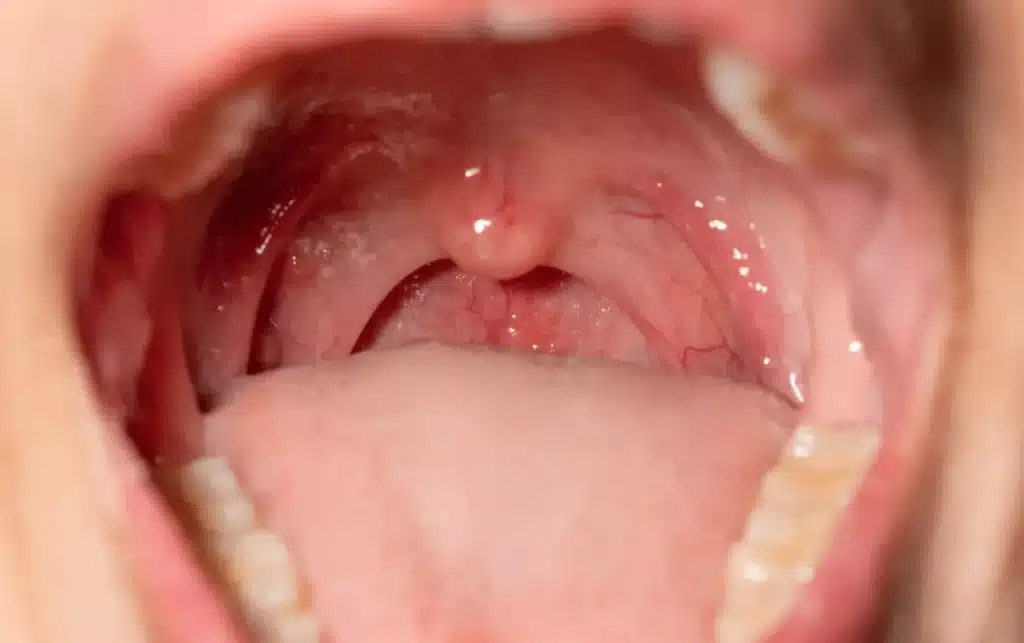
Introduction:
Tooth infections, also known as dental abscesses, can be painful and potentially dangerous if left untreated. While the primary symptoms of a tooth infection are localized to the affected area, it is important to recognize that the infection can spread beyond the tooth and jaw. If bacteria from a dental abscess enter the bloodstream, it can lead to a condition known as sepsis, which is a life-threatening infection. In this article, we will explore the symptoms of a tooth infection spreading to the body, emphasizing the importance of early detection and treatment to prevent complications.
Swelling and Pain:
One of the first signs that a tooth infection is spreading beyond the tooth and jaw is an increase in swelling and pain. Initially, the swelling and pain may be localized to the infected tooth and its surrounding area. However, as the infection progresses, the swelling can spread to other parts of the face, neck, or even the head. The pain can become more intense and persistent, and it may radiate to other areas of the body.
Fever and Chills:
As the infection spreads, the body’s immune response kicks in, resulting in a fever. A persistent high-grade fever, often accompanied by chills and sweating, can indicate that the infection has reached a more severe stage. The body’s elevated temperature is a sign that the immune system is fighting the infection, but it also indicates that the infection has spread beyond the tooth.
Fatigue and Malaise:
Tooth infections that spread to the body can cause a general feeling of fatigue and malaise. The body’s immune response to the infection requires a significant amount of energy, leading to a feeling of tiredness and weakness. Individuals may experience a lack of energy, reduced motivation, and a general sense of unwellness. If these symptoms persist, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention.
Lymph Node Swelling:
When a tooth infection spreads, it can cause the lymph nodes in the neck and jaw area to become swollen and tender. The lymph nodes play a crucial role in the body’s immune response and become enlarged as they work to fight off the infection. Palpating the lymph nodes in the neck and jaw area may reveal tenderness and swelling, indicating the spread of the infection.
Headaches and Dizziness:
As the infection progresses, it can affect the surrounding tissues, including the sinuses and the bones of the skull. This can lead to headaches, migraines, and dizziness. The pain may be localized or spread throughout the head and can be accompanied by pressure and a sense of heaviness. If you experience severe or persistent headaches along with other symptoms of a tooth infection, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Rapid Heart Rate and Elevated Blood Pressure:
In severe cases where the infection has spread to the bloodstream, individuals may experience an increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure. These symptoms are indicative of a systemic response to the infection and should not be ignored. If you notice a rapid heartbeat or an increase in blood pressure, it is vital to seek emergency medical care.
Organ Dysfunction and Sepsis:
If a tooth infection is left untreated or not properly managed, it can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition. Sepsis occurs when the infection spreads throughout the body, affecting multiple organs and systems. Symptoms of sepsis include confusion, difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, abdominal pain, and a drop in blood pressure. If sepsis is suspected, immediate medical attention is crucial.
Prevention and Treatment of Tooth Infection Spreading to the Body:
Tooth infections can be both painful and potentially dangerous if left untreated. When a tooth infection spreads beyond the tooth and jaw, it can lead to severe complications. To prevent the spread of infection to the body, it is essential to practice good oral hygiene, seek prompt dental care, and undergo appropriate treatment.
We will discuss effective prevention strategies and available treatment options for preventing and managing the spread of tooth infections to the body.
Prevention:
- Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene:
Practicing good oral hygiene is the first line of defense against tooth infections. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help remove plaque and bacteria that can lead to infections. Regularly visiting your dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups is also crucial for early detection and prevention of dental issues.
- Address Dental Issues Promptly:
Any signs of dental problems, such as tooth decay, gum disease, or cracked teeth, should be addressed promptly. Ignoring these issues can lead to tooth infections. If you experience tooth pain, sensitivity, or any other dental concerns, consult your dentist as soon as possible for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
- Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle:
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall oral health and reduce the risk of tooth infections. Avoiding tobacco use, limiting alcohol consumption, and following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and calcium-rich foods can help strengthen teeth and support the immune system.
- Wear Protective Gear:
If you participate in contact sports or activities that pose a risk of dental trauma, wearing protective gear, such as mouthguards or helmets, can help prevent injuries that may lead to tooth infections.
Treatment:
- Dental Abscess Drainage:
When a tooth infection spreads to the body, it is crucial to drain the abscess to remove the source of infection. This procedure is typically performed by a dentist or an oral surgeon, who will make an incision in the affected area to allow the pus to drain. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to eliminate the remaining infection.
- Root Canal Therapy:
If the tooth infection has reached the pulp of the tooth, root canal therapy may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning the root canals, and sealing them to prevent further infection. Root canal therapy can save the tooth from extraction and prevent the infection from spreading.
- Tooth Extraction:
In severe cases where the tooth infection is extensive and cannot be effectively treated with root canal therapy, tooth extraction may be necessary. This is performed to remove the infected tooth and prevent the spread of infection to neighboring teeth and the body. After extraction, appropriate measures will be taken to promote healing and restore dental function.
- Antibiotic Treatment:
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to eliminate the infection and prevent its spread to other parts of the body. The specific type of antibiotic and duration of treatment will depend on the severity of the infection and individual factors. It is crucial to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the dentist or healthcare provider.
- Supportive Measures:
In addition to specific treatments, supportive measures such as pain management, warm saltwater rinses, and maintaining good oral hygiene are important for relieving discomfort, promoting healing, and preventing further infection.
Conclusion:
Recognizing the symptoms of a tooth infection spreading to the body is vital for early detection and appropriate treatment. Swelling and pain, fever and chills, fatigue and malaise, lymph node swelling, headaches and dizziness, rapid heart rate and elevated blood pressure, and organ dysfunction are all potential indicators that a dental infection has progressed beyond the tooth and jaw. It is essential to seek immediate dental and medical care to prevent further complications, including sepsis. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene, and prompt treatment of dental infections are essential in maintaining good oral health and preventing the spread of infection to the body.
Prevention and prompt treatment are key to avoiding the spread of tooth infections to the body. By maintaining excellent oral hygiene, addressing dental issues promptly, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and wearing protective gear when necessary, the risk of tooth infections can be significantly reduced. In case of a tooth infection spreading to the body, timely dental intervention, which may include abscess drainage, root canal therapy, tooth extraction, and antibiotic treatment, can effectively manage the condition and prevent complications. Remember to consult with a professional dentist near your area for proper diagnosis, guidance, and personalized treatment options.