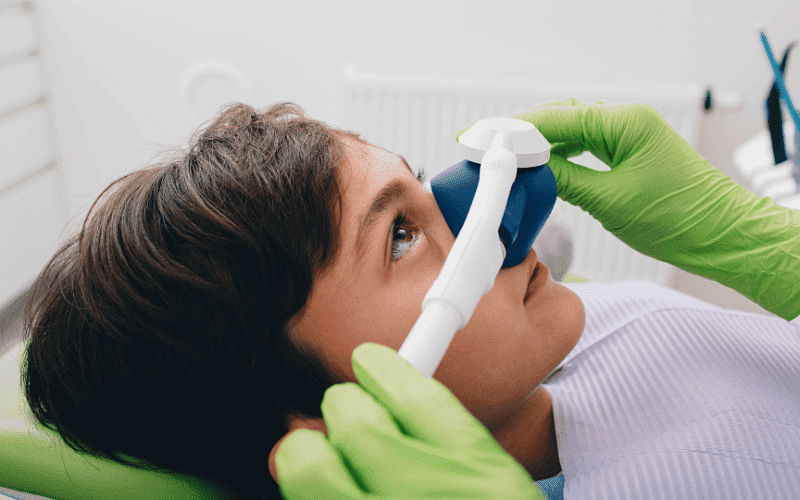
A dentist appointment can be stressful, but the development of dental oral sedation promises a more pleasant encounter. This innovative treatment employs well-selected drugs to generate a soothing effect, changing the dentist’s chair into a haven of relaxation. However, like any medical intervention, there is a complex terrain of possible adverse effects. This investigation delves into the secrets of dentistry oral sedation, shedding light on its science and digging into common and uncommon adverse effects. Join us on a journey of discovery that will equip you to make educated decisions about your dental health.
The Science Behind Dental Oral Sedation:
Before we examine the potential side effects, let’s look at how dentistry oral sedation works. Dentists commonly use benzodiazepines or anti-anxiety medicines to promote a state of calm. These drugs act on the central nervous system, causing a soothing effect that assists patients in managing anxiety during dental operations.
Common Side Effects:
1. Nitrous Oxide Adverse Reactions:
Nitrous oxide, popularly known as laughing gas, is a popular and safe method of dental oral sedation, although it can have major adverse effects in certain individuals. Some symptoms include nausea, vomiting, headaches, fainting, fuzzy vision, sleepiness, and excessive shivering or sweating. The most prevalent negative effects come when the patient’s nitrous oxide level is too high, making it a potentially dangerous medicine for youngsters and some patients.
2. Oral Sedation:
Dental oral sedation is a therapeutic option for individuals who have significant dental phobias or anxieties, allowing them to get treatment without fear or worry. Anti-anxiety medicine is given to patients one night before and again a few hours before the surgery. The most common adverse effects include forgetting the operation, having trouble driving home, and failing to follow care recommendations. This technique requires the presence of a responsible adult, as well as sleepiness, dry mouth, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and headaches.
3. Sedation By IV:
IV sedation is a type of dental sedation that is used in severe cases of phobia or for extensive or lengthy dental procedures. It entails injecting medicines intravenously into veins. Minor bruising, swelling, and bleeding are risks, as are falling asleep during the treatment, not being aware of your surroundings, forgetting care instructions, and having difficulties driving home. This technique requires the presence of a responsible adult. Drowsiness, dry mouth, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and headaches are all possible adverse effects.
4. Memory Loss:
Some patients may experience temporary memory loss or difficulty recalling dental oral sedation procedure details. This is usually a short-term effect, but discussing concerns with your dentist is essential.
5. Allergic Reactions:
Though uncommon, allergic reactions to sedative medications can occur. Dentists carefully evaluate patients’ medical histories to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Less Common Side Effects:
While the vast majority of individuals suffer relatively minor and transient side effects, others may face less common but possibly more significant issues:
1. Respiratory Depression:
In rare situations, dental oral sedation can cause respiratory depression, in which breathing becomes slower or shallower than normal. Patients with pre-existing respiratory issues are more prone to experience this.
2. Cardiovascular Effects:
Some sedatives may have cardiovascular effects, altering blood pressure and heart rate. Dentists regularly check these vital signs throughout treatments to ensure patient safety.
3. Delayed Recovery:
Some people may notice a prolonged recovery from dental oral sedation, taking longer to feel completely aware than normal. This is more prevalent among older adults.
Tips to overcome dental sedation side effects
1. Follow Post-Procedure Guidelines:
Adhere strictly to the post-operative instructions provided by your dentist. These guidelines often include restrictions on driving, operating machinery, or engaging in strenuous activities for a certain period. Compliance with these recommendations helps minimize the risk of accidents or complications associated with lingering sedation effects.
2. Stay Hydrated:
Drinking plenty of water is essential to flush the sedative agents from your system—hydration aids in eliminating residual medication reducing the duration of side effects. Additionally, maintaining proper hydration helps counteract potential dry mouth, a common side effect of some sedatives.
3. Rest and Allow Recovery Time:
Plan for adequate rest after a dental procedure involving sedation. Fatigue and drowsiness are typical side effects, and giving your body time to recover is crucial. Avoid overexertion, and take the remainder of the day off to allow your body to metabolize the sedative medication fully.
4. Avoid Alcohol and Certain Medications:
Steer clear of alcohol and medications that could potentially interact with the sedative agents. Combining sedatives with substances that depress the central nervous system can amplify side effects and pose health risks. Always consult your dentist or healthcare provider regarding the safety of any medications or substances post-sedation.
5. Communicate Any Concerns Promptly:
If you experience persistent or severe side effects after dental sedation, promptly communicate with your dentist or healthcare provider. Open and honest communication is key to addressing concerns and obtaining guidance on managing side effects. Your healthcare team can provide appropriate recommendations, reassurance, or additional interventions if necessary.
Oral sedation appears as a transformational tune in the symphony of dental care, arranging calm amid procedural anxiety. While the benefits are clear, awareness of potential negative effects is critical. As we end our voyage, remember that proactive communication with your dentist is the key to virtuoso performance. Dental oral sedation is a strong instrument with a potential symphony of sleepiness and uncommon crescendos of respiratory concerns. You conduct your oral health story by wielding information, embracing the symphony of sedation with wisdom, and ensuring that your dental journey stays a harmonic crescendo of well-informed decisions and enduring smiles.
Also, read our other article: Is Dental Sedation The Same As Anesthesia?